|
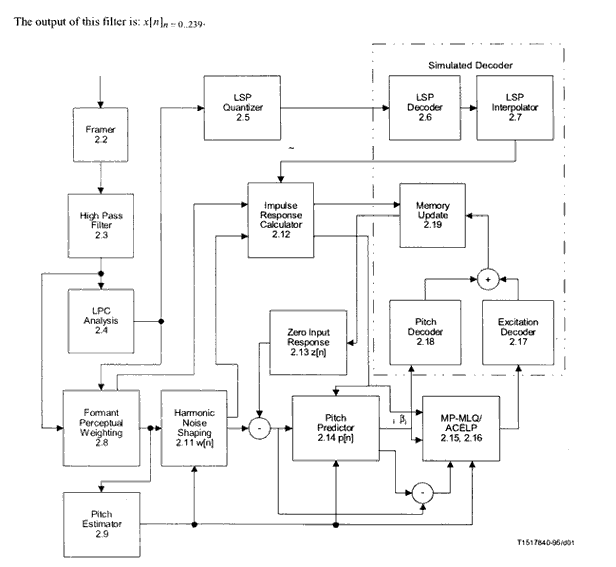
The encoder operates on frames of 240 samples (30ms) each. Each frame is first high pass filtered to remove DC component and then divided into 4 subframes of 60 samples (7.5ms) each. For every subframe, a 10th order Linear Prediction Coder (LPC) filter is computed. The LPC filter for the last subframe is quantized using a Predictive Split Vector Quantizer (PSVQ). The unquantized LPC coefficients are used to construct the short-term perceptual weighting filter. The weighting filter is used to filter the entire frame and to obtain the perceptually weighted speech signal. Every two subframes the open loop pitch period (pitch estimation in the range from 18 to 142 samples) is computed using the weighted speech signal. From this point speech is processed at subframe basis. The estimated pitch period is used to construct the harmonic noise shaping filter. The combination of LPC synthesis filter, perceptual weighting filter, and the harmonic noise shaping filter is used to create an impulse response. Using this impulse response and the pitch period estimation a closed loop pitch predictor (5th order) is computed. The pitch period is computed as a small differential value around the open loop pitch estimate. Both the pitch period and the differential value are transmitted to the decoder. Finally the non-periodic component of the excitation is approximated. For high rate, Multi-Pulse Maximum Likelihood Quantization (MP-MLQ) excitation is used, and for lower bit rate, an algebraic-code-excitation (ACELP) is used.
The major differences between the two rates are in the pulse positions and amplitude coding. Also at the lower rate 170 codebook entries are always used for the gain vector of the long term predictor. |