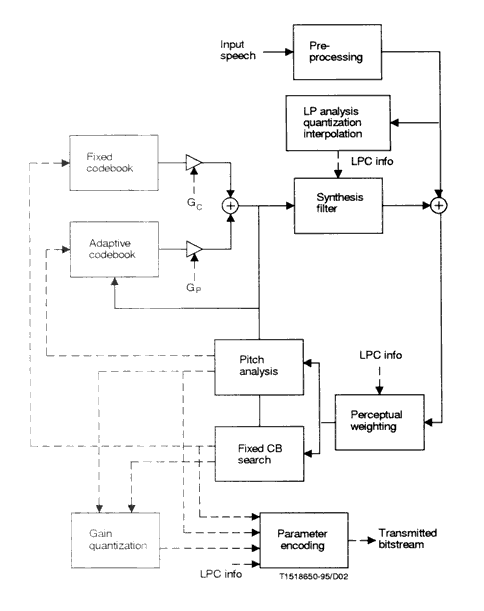
Ref. [4],Figure 2
The digital input signal is high-pass filtered and scaled in the pre-processing block. LP analysis is done once per 10 ms (80 samples) to compute the LP filter coefficients. Those coefficients are converted to Line Spectrum Pairs (LSP) and quantized using predictive two-stage Vector Quantization (VQ) with 18 bits. The excitation signal is chosen by using an analysis-synthesis search procedure in which the error between the original and reconstructed speech is minimised according to a perceptually weighted distortion measure. Therefore the error signal is filtered with a perceptual weighting filter, whose coefficients are derived from the unquantized LP filter. The amount of perceptual weighting is made adaptive to improve the performance for input signals with flat frequency-response.
The excitation parameters are determined per subframe of 5 ms (40 samples). An open-loop pitch delay is estimated once per 10 ms frame based on the perceptually weighted speech signal. The following operations are repeated for each subframe. Closed-loop pitch analysis is done to find the adaptive–codebook delay and gain, by searching around the value of the open-loop pitch delay. The pitch delay is encoded with 8 bits in the first subframe and differentially encoded with 5 bits in the second subframe. The target signal (perceptually weighted LP residual) is updated by subtracting the (filtered) adaptive–codebook contribution, and this new target is used to in the fixed-codebook search to find the optimum excitation. An algebraic codebook with 17 bits is used for the fixed –codebook excitation. The gains of both codebooks are vector quantized with 7 bits, whereby moving average prediction is applied to the fixed-codebook gain.