
An H.323 terminal is an endpoint on the local area network which enables real-time, two-way communications with another H.323 terminal, gateway, or MCU. Any terminal may provide voice only, voice and data, voice and video, or voice, video and data. H.323 specifies the mode of operation for each type of terminal.
All H.323 terminals must support these features:
H.323 terminals may optionally support these features:
Gateways are found where network administrators need to:
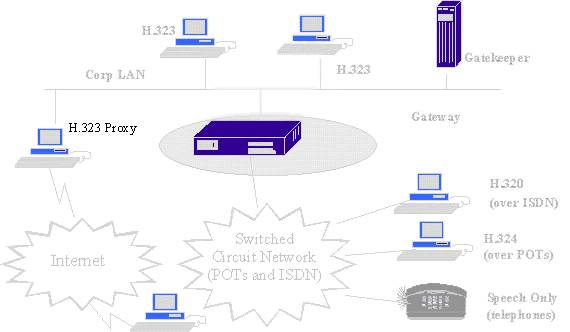
A specialized gateway is a proxy gateway, which is a secured connection between H.323 sessions. It contains a proxy feature as part of the conference infrastructure that can provide QoS, traffic shaping, and security and policy management for H.323 traffic across secured connection.
Also an optional component, gatekeepers provide call control services to H.323 endpoints. One or more gatekeepers may be deployed, and are logically separate from the endpoints. While standards for gatekeeper-to-gatekeeper communications are not established, the physical implementation may coexist with a terminal, MCU, gateway, MC or other non-H.323 LAN devices.
Gatekeepers can provide these services:
A multipoint controller (MC) is a LAN-based H.323 entity that controls three or more terminals participating in multipoint conferences. It may also control a point-to-point conference which may develop into a multipoint conference. An MC provides capabilities negotiation with all terminals to establish common levels of communication. It may also control conference resources such as multicast video. An MC does not mix or switch audio, video and data.
A multipoint processor (MP) is a LAN-based H.323 entity that centrally processes audio, video, and/or data streams in a multipoint conference. The MP mixes, switches, and performs other processing duties for streams controlled by an MC. It may process one or many media streams depending upon the type of conference it is supporting.
A multipoint control unit (MCU) supports multipoint conferences between three or more endpoints. As defined by H.323, an MCU consists of a required MC and optional MP's. A typical MCU supporting centralized multipoint conferences consists of an MC unit, and an MP that supports audio, video, and data streams.
The H.323 recommendations allow either centralized or decentralized conference configurations, an MCU is required for the first, while the second can be administrated with multicast technologies.